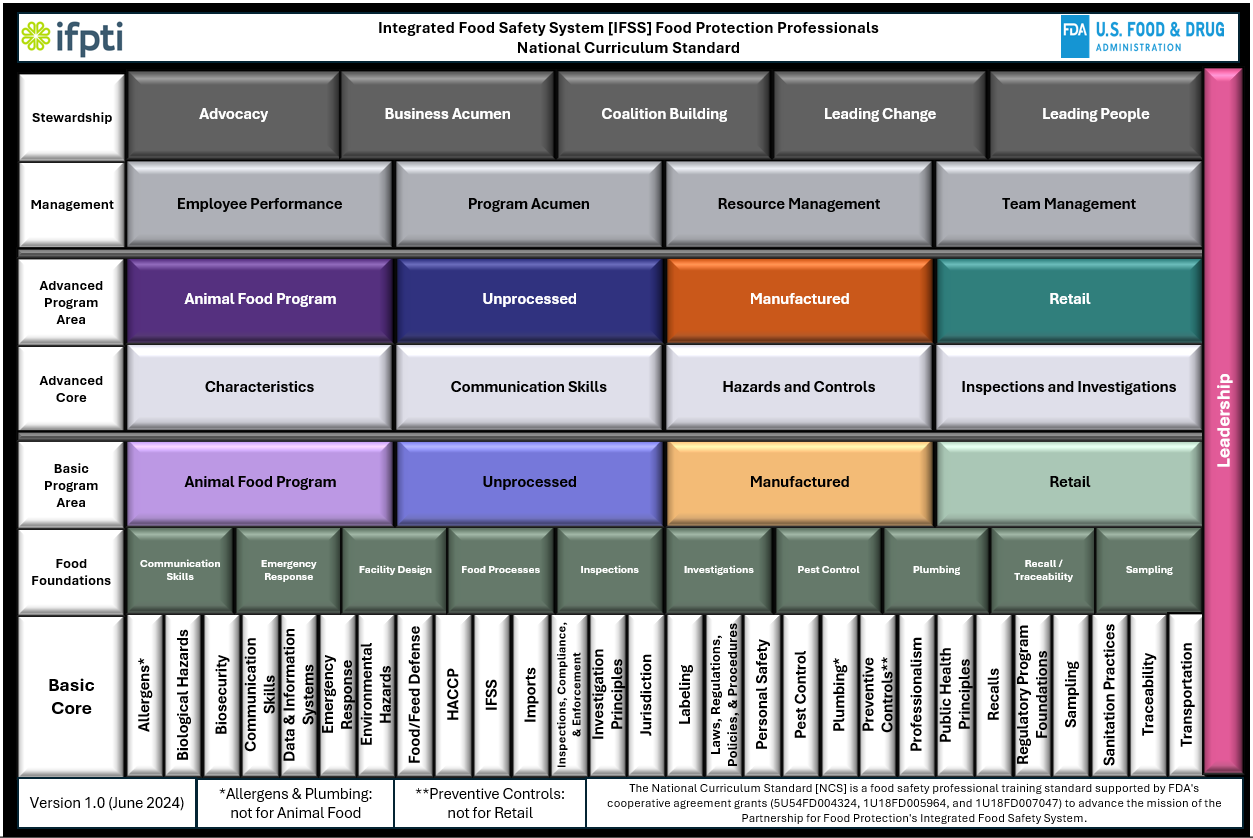
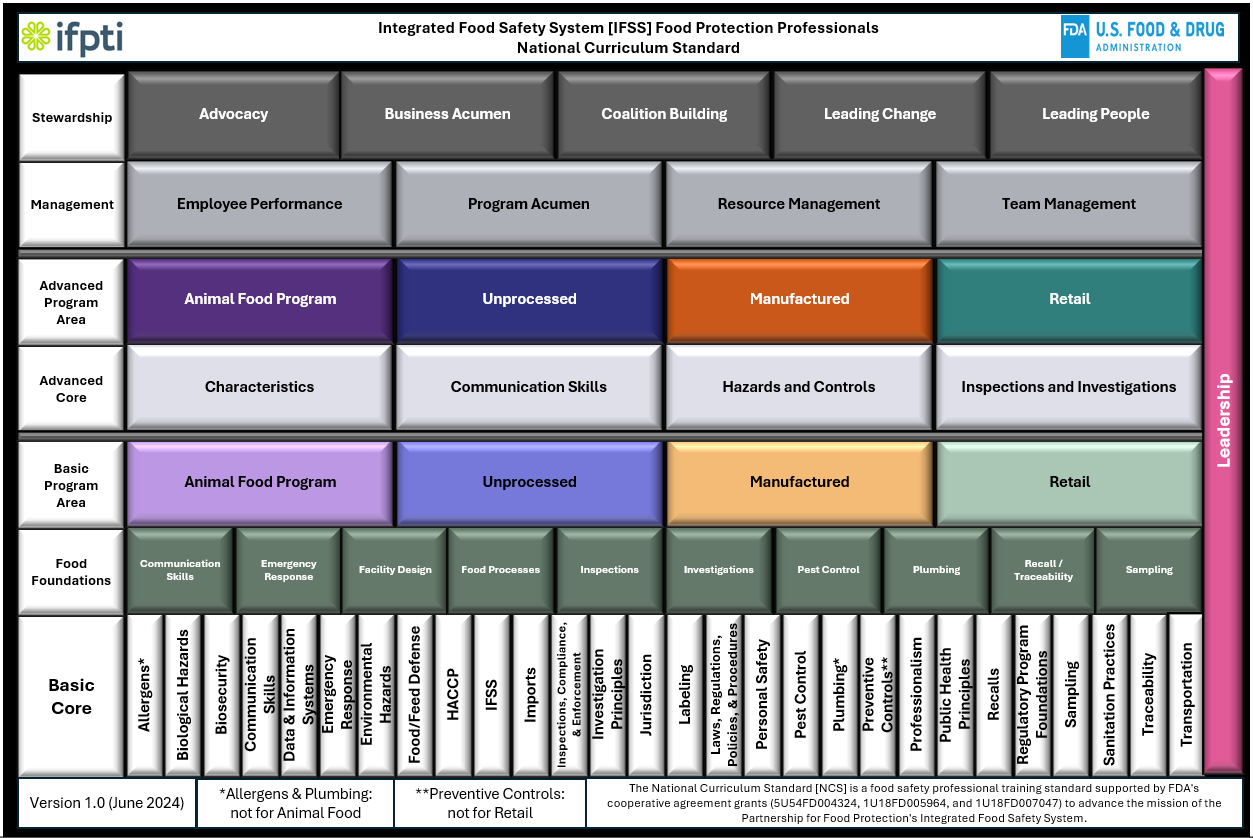
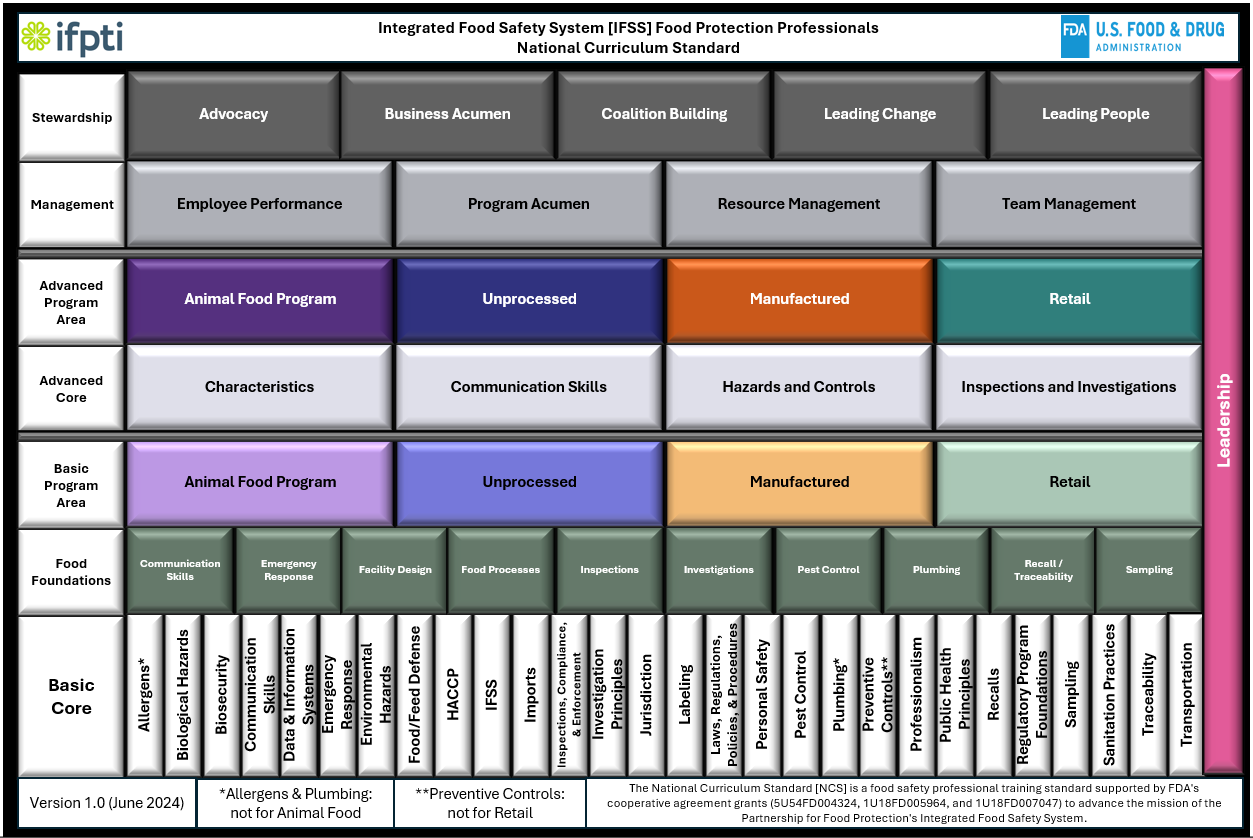
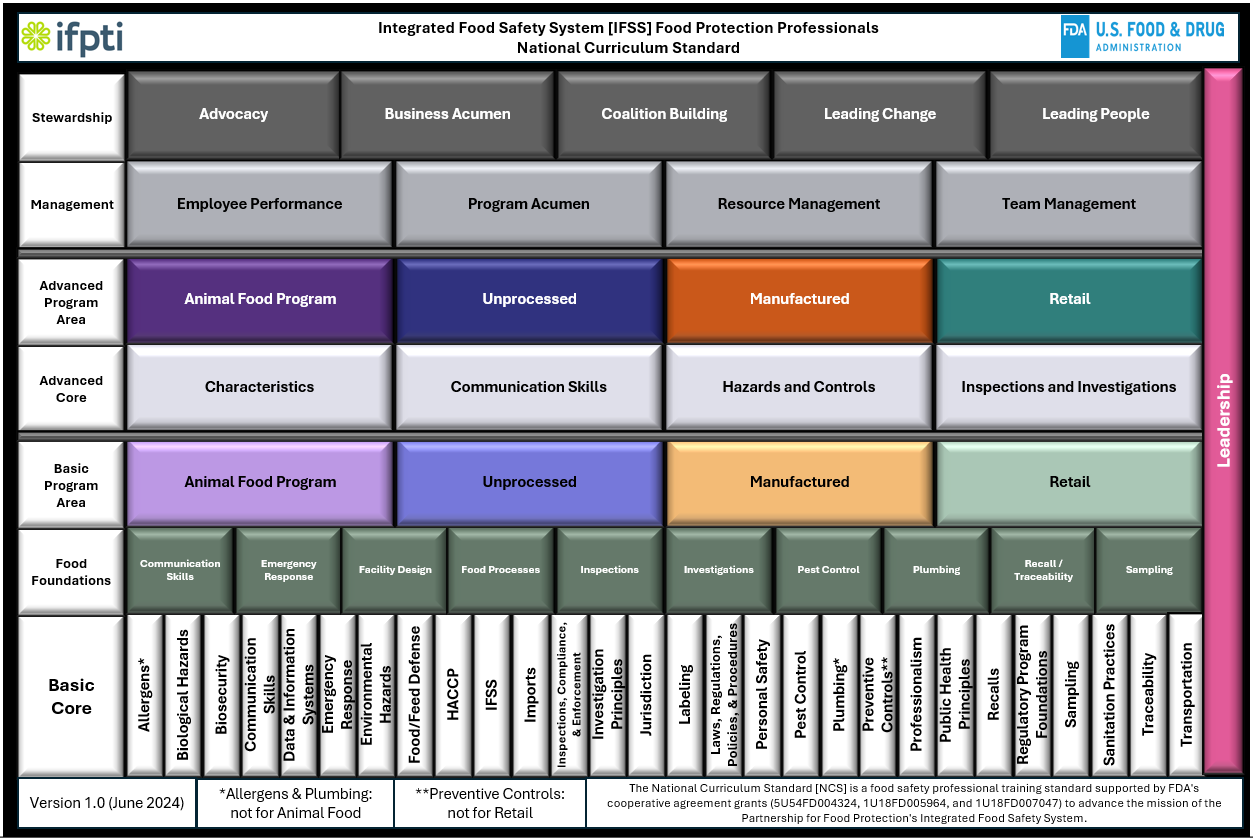
Biological Hazards
The IFSS Basic Level Biological Hazards provides introductory knowledge, skills, and abilities related to biological hazards, focusing on sources of contamination, growth factors, and control methods.
Goal: The student will be able to explain the properties of biological hazards.
Scope: The topics in this course include foundations, biological hazards of concern, growth factors, sources and pathways, control factors.
Course Objectives
Foundations
Define relevant terminology.
Describe the impact of biological hazards on food production.
Distinguish between pathogens and spoilage organisms.
Describe where to find resources.
Give an example of how a milestone outbreak impacted public policy.
Discuss how sampling is used to detect organisms of concern.
Give examples of illness caused by biological hazards.
Biological Hazards of Concern
Identify categories of biological hazards.
Give examples of each category of biological hazard.
Compare characteristics of bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi and other biological agents.
Associate biological hazards with products and processes.
Growth Factors
Differentiate between the growth factors of biological organisms.
Describe the effects of environmental conditions on growth.
Discuss how normal flora competition can inhibit pathogen growth.
Sources and Pathways
Discuss how biological hazards contaminate products and processes.
Describe vectors of contamination.
Give examples of food contamination sources.
Differentiate between direct and indirect food contact surfaces
Give examples of feed contamination sources.
Differentiate between intentional and unintentional contamination.
Control Factors
Differentiate between control factors for biological hazards.
Explain the concept of FATTOM to prevent the growth of biological hazards.
Describe how product packaging can limit or prevent the growth of biological hazards.
Describe control point monitoring.
Explain why source is important as a control factor.
Describe best management practices that are used to prevent spread of biological hazards.
Explain the concept of “hurdle factors”.
Give examples of organism-specific control factors.
Duration
Unit 1: Foundations - 25 minutes
Unit 2: Biological Hazards of Concern – 41 minutes
Unit 3 – Growth Factors Introduction – 19 minutes
Unit 4: Sources and Pathways – 30 minutes
Unit 5: Control factors – 87 minutes
Total course estimate – 3 hours and 22 minutes
The IFSS Basic Level Biological Hazards provides introductory knowledge, skills, and abilities related to biological hazards, focusing on sources of contamination, growth factors, and control methods.
Goal: The student will be able to explain the properties of biological hazards.
Scope: The topics in this course include foundations, biological hazards of concern, growth factors, sources and pathways, control factors.
Course Objectives
Foundations
Define relevant terminology.
Describe the impact of biological hazards on food production.
Distinguish between pathogens and spoilage organisms.
Describe where to find resources.
Give an example of how a milestone outbreak impacted public policy.
Discuss how sampling is used to detect organisms of concern.
Give examples of illness caused by biological hazards.
Biological Hazards of Concern
Identify categories of biological hazards.
Give examples of each category of biological hazard.
Compare characteristics of bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi and other biological agents.
Associate biological hazards with products and processes.
Growth Factors
Differentiate between the growth factors of biological organisms.
Describe the effects of environmental conditions on growth.
Discuss how normal flora competition can inhibit pathogen growth.
Sources and Pathways
Discuss how biological hazards contaminate products and processes.
Describe vectors of contamination.
Give examples of food contamination sources.
Differentiate between direct and indirect food contact surfaces
Give examples of feed contamination sources.
Differentiate between intentional and unintentional contamination.
Control Factors
Differentiate between control factors for biological hazards.
Explain the concept of FATTOM to prevent the growth of biological hazards.
Describe how product packaging can limit or prevent the growth of biological hazards.
Describe control point monitoring.
Explain why source is important as a control factor.
Describe best management practices that are used to prevent spread of biological hazards.
Explain the concept of “hurdle factors”.
Give examples of organism-specific control factors.
Duration
Unit 1: Foundations - 25 minutes
Unit 2: Biological Hazards of Concern – 41 minutes
Unit 3 – Growth Factors Introduction – 19 minutes
Unit 4: Sources and Pathways – 30 minutes
Unit 5: Control factors – 87 minutes
Total course estimate – 3 hours and 22 minutes
The IFSS Basic Level Biological Hazards provides introductory knowledge, skills, and abilities related to biological hazards, focusing on sources of contamination, growth factors, and control methods.
Goal: The student will be able to explain the properties of biological hazards.
Scope: The topics in this course include foundations, biological hazards of concern, growth factors, sources and pathways, control factors.
Course Objectives
Foundations
Define relevant terminology.
Describe the impact of biological hazards on food production.
Distinguish between pathogens and spoilage organisms.
Describe where to find resources.
Give an example of how a milestone outbreak impacted public policy.
Discuss how sampling is used to detect organisms of concern.
Give examples of illness caused by biological hazards.
Biological Hazards of Concern
Identify categories of biological hazards.
Give examples of each category of biological hazard.
Compare characteristics of bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi and other biological agents.
Associate biological hazards with products and processes.
Growth Factors
Differentiate between the growth factors of biological organisms.
Describe the effects of environmental conditions on growth.
Discuss how normal flora competition can inhibit pathogen growth.
Sources and Pathways
Discuss how biological hazards contaminate products and processes.
Describe vectors of contamination.
Give examples of food contamination sources.
Differentiate between direct and indirect food contact surfaces
Give examples of feed contamination sources.
Differentiate between intentional and unintentional contamination.
Control Factors
Differentiate between control factors for biological hazards.
Explain the concept of FATTOM to prevent the growth of biological hazards.
Describe how product packaging can limit or prevent the growth of biological hazards.
Describe control point monitoring.
Explain why source is important as a control factor.
Describe best management practices that are used to prevent spread of biological hazards.
Explain the concept of “hurdle factors”.
Give examples of organism-specific control factors.
Duration
Unit 1: Foundations - 25 minutes
Unit 2: Biological Hazards of Concern – 41 minutes
Unit 3 – Growth Factors Introduction – 19 minutes
Unit 4: Sources and Pathways – 30 minutes
Unit 5: Control factors – 87 minutes
Total course estimate – 3 hours and 22 minutes